History of Banking Sector in Cambodia
1975: During the rule of Khmer Rouge in Cambodia
- All banks were closed.
- Money was abolished.
1979: End of Khmer Rouge Rule and Transition
- The National Bank of Cambodia (NBC) was established as the central bank.
- The Foreign Trade Bank was to provide commercial banking services.
- Cambodia currency, the Riel, was introduced in 1980.
1992 – 1998: Privately Owned and Foreign Subsidiaries
- Foreign subsidiaries initially required minimum. capital of $5 million and 15% owned by the NBC.
- By 1998, 32 commercial banks were licensed.
1998 – 2001: Banking Sector Reforms
- Introduced under the new Governor H.E. Chea Chanto.
- Abolishment of required 15% NBC stake in private owned/ foreign banks.
- Classification of financial institutions into three categories: Full Commercial Banks (min. $13 million paid-up capital), Specialized Banks (min. $2.5 million paid-up capital), and Licensed/Registered Microfinance Institutions (MFIs).
2002 – 2008: Extension of the Banking Sector
- The Banking Sector Reform process continues.
- The Foreign Trade Bank was privatized.
- New foreign banks arrived particularly from Australia, Korea, and Japan.
- Requirement of $37.5 million minimum. capital for Commercial Banks by not later than the end of 2010.
- Countermeasures set by NBC against over liquidity given the inflation pressure and the global credit crisis in 2008.
- Became a member of Asia Pacific Group (APG) on Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism.
- Declared the enforcement of the Law on Anti-Money Laundering and Combating the Financing of Terrorism.
- Becoming the 15th member of South-east Asia Central Bank (SEACEN).
- 4 local banks initiated to use ATMs and Internet Banking in Cambodia.
- Renovated the Credit Information Sharing system.
2009 – 2015: Banking Digitalization
- Launching of mobile banking in the early of 2009.
- Introduced an accommodative monetary policy in early 2009 by reducing the reserve requirement ratio on foreign currency deposit from 16% to 12 %.
- Establishment of Cambodia Financial Intelligence Unit (CAFIU) on Money laundering and combating the financing of terrorism.
- Officially launched the National Payment System in December 2012. The NBC also installed the Client Module system at its headquarters, connecting 38 members banks to the National Payment System at the National Clearing House.
- Developed the “Shared Switch” system to expand the payment system, to support the integration of Banks´ ATMs, and to facilitate the payment by mobile phone and internet.
2016 – 2017
- Became the 7th of 190 countries for “ease of access to loan” by World Bank Doing Business Magazine report, release in the late of 2016.
- Launch of the new payment system, called “FAST Payment” to allow customers to transfer local currency from one bank account to another instantaneously.
- Introduction of the “Online Banking System” with 21 members including 14 commercial banks, 1 specialized bank, and 6 microfinance deposition institution, in 2016.
- A total of 26 hotline numbers were introduced in the capital and all provinces to answer general inquiries from the public regarding financial services.
- Launch of the “Cambodian Shared Switch” and study on gross fast payment system with the potential accessibility of Digital currencies for inter-bank transactions.
2018 – Present
- The Association of Banks in Cambodia has 66 members, comprising by 45 commercial banks, 16 specialized banks, 4 representative offices and 1 Cambodia Microfinance Association.
- The Institute of Banking and Finance (IBF) has provided a series of training courses to strengthen the capacity and professionalism of the Banking and Finance Officers, with around 200 officials of the Banking and Finance Institutions being granted certificates.
- On the 29th March 2019, the official launch of CSF Principles with the adoption by 49 member banks and the endorsement by NBC and the Ministry of Environment took place.
- On the 16thMay 2019, the National Bank of Cambodia announces the accession of a Fast and Swap System.
- ABC adopted a single standard AID, VISA Spec to make it easy for all members to use the comprehensive, convenient and secure payment system together.
- NBC with support of ABC developed the National Payment network using Blockchain Technology to promote cross-payment and regional transactions.
- ABC amended its statutes to encourage the participation from all banking and financial institutions and payment
Banking Environment
Cambodia is a bank-based economy. Commercial banks are the primary source of funding. The Cambodian banking system is a two-tier system comprising the Central Bank (National Bank of Cambodia), and private sectors such as commercial banks, specialized banks, microfinance institutions, and a number of NGOs involved in rural credit activities.
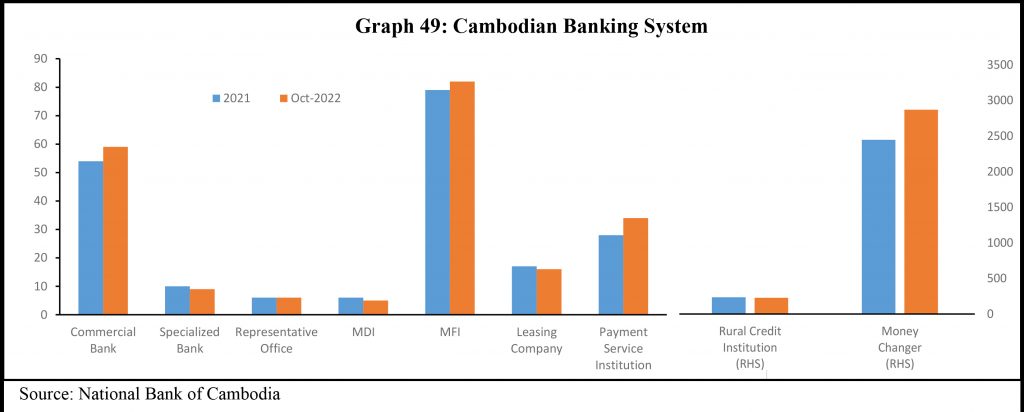
The Cambodian Banking System consists of 59 Commercial Banks, 9 Specialized Banks, 5 Microfinance Deposit-Taking Institutions (MDIs), 82 Non-Deposit-Taking Microfinance Non-Deposit-Taking Institutions (MFIs), 224 Rural Credit Institutions, 16 Financial Leasing Companies, 34 Payment Service Institutions, 6 Representative Offices of Foreign Banks, and 2,869 Money Exchange Agents.
Recent liberal investment regime and open market trade policies have gathered momentum for Cambodia’s economic prospects and banks are also enjoying benefits from such strong growth opportunities. The Cambodian banking sector has been improving and growing steadily over the past two decades; yet; it still lacks of financial depth and is being fragmented. To gain more international confidence, significant progresses are necessitated to address structural distortions such as inadequate legal framework for secured transactions, and information asymmetry arising from poor disclosure standards.
Banking Services
As the banking sector’s growth continues to accelerate and increase in sophistication, new banking products and services are also developed. Leasing and hire purchase products have been increasingly and prevalently used mainly for consumer goods financing. Both bank centric and mobile banking centric models are operating in Cambodia. Regardless of models or forms, mobile banking businesses are restricted and subject to the regulation and supervision of the National Bank of Cambodia to ensure the protection of customers.
Currently the following banking services are offered:
- Deposits (savings, current and fixed accounts) in KHR, USD, THB, Euro. etc.
- Loans: Commercial, SMEs, Housings, Consumers
- Guarantee Service
- Trustee Service
- Foreign Exchange
- Travelers Cheques
- Trade Finance: Letter of Credit
- Local and international money transfer
- ATM Service
- International Credit Cards
Impacts of Banking Sector
90 percent of Cambodia’s financial assets are located in the country’s banking system. Last year (2018) the Bank´s assets increased by 20.12 percent to approximately USD28.89 billion, equivalent to 131.43 percent of GDP. Credit was concentrated in key economic sectors such as wholesales and retails (30 percent), agriculture (10.40 percent), construction (9.50 percent), residential real estate loan (9.30 percent), and other sector (40.80 percent). At the same time, banks’ deposit grew at a rate of 25.11 percent, an increase of 3.29 percentage point from 2016, making total deposit amount stood at USD17.42 billion.
Non-performing loans ratio remained at 2.40 percent in 2017 compared to 2016. The banking industry’s Return on Asset (ROA) and Return on Equity (ROE) were 1.54 percent and 8.40 percent, respectively.
Cambodia’s banking sector is expanding rapidly. By the end of 2017, the sector has 39 commercial banks, 15 specialized banks, 69 microfinance institutions, seven microfinance deposit-taking institutions, 313 rural credit institutions, six representative offices, 11 financial lease companies, six third party processors, nine payment service providers, one credit bureau company, and 2,478 money changers . In addition, total number of credit and debit cards increased to 74,130 and 1,813,435 cards respectively.
In 2017, banking operations have launched 44 new branches, and 273 new ATM terminals in addition to the existing 1,260 ATM machines.